8 Natural Brightening Alternatives to Hydroquinone

Hoping to lighten up scarring, freckles or dark spots on your skin? You’ve got plenty of options, from natural brightening ingredients to prescription treatments.
You may have heard that hydroquinone—a brightening agent—is strong enough to get the job done. While it’s true that it’s a powerful ingredient, the Food and Drug Administration has banned the sale of over-the-counter hydroquinone due to rising concerns over side effects from its use.
Luckily, there are many natural alternatives that can lighten dark spots and hyperpigmentation, giving you results that rival those of harsher treatments—without the harmful effects.
Here, we’ll help you get up to speed on the best ingredients to target concerns from post-acne marks to sun spots for your clearest skin yet.
Why You Should Consider Natural Lighteners for Dark Spots
Products with natural ingredients have become more popular as the safety of hydroquinone has come into question.
“Hydroquinone is one of the most researched and studied lightening agents, but can cause severe irritation and hyperpigmentation if not used correctly,” explains Dr. Michele Green, a board-certified dermatologist and RealSelf contributor in New York City.
For this reason, it’s best to avoid ingredients like hydroquinone or corticosteroids (such as hydrocortisone) unless prescribed by a board-certified dermatologist.
Hydroquinone-free lightening agents are an effective alternative. According to Dr. Robin Evans, a board-certified dermatologist in Stamford, CT, “These products can help with brightening, smoothing the skin and exfoliating. They can also help with pigmentary concerns like melasma.”
How Do Natural Dark Spot Lighteners Work?
If you’re ready to try a new wave of natural skin brighteners, consider the following dermatologist-approved ingredients.
1. Kojic Acid
Kojic acid is derived from mushroom-like fungi during fermentation and is the second most common natural lightening agent, Dr. Green says. “It prohibits the production of melanin and penetrates the upper layers of the skin, causing a lightening effect.”
You can find kojic acid in serums and brightening creams. Note, it can cause some side effects like redness and irritation. Always use a low-dose (1 percent) version and test it on a small patch of your skin first before using regularly.
Try:SkinCeuticals Discoloration Defense
2. Niacinamide
Niacinamide, or vitamin B3, is a gentle yet powerful skin care ingredient that offers a multitude of benefits. As Dr. Green explains, “During the process of skin pigmentation, melanin is synthesized by skin cells called melanocytes. The melanin that is produced is transferred inside particles called melanosomes, to skin cells called keratinocytes. Keratinocytes store the melanin and use it as a protective shield for the cell DNA against UV rays. Niacinamide helps reduce hyperpigmentation, brightening the skin by inhibiting the transfer of melanosomes from melanocytes to keratinocytes.”
What’s more, she says, it is extremely stable and not affected by heat or light like other chemical ingredients. Niacinamide is found in serums and boosters that are usually considered safe to use daily.
Try:SkinMedica Lytera 2.0 Pigment Correcting Serum
3. Vitamin C
Vitamin C is another popular brightening alternative found in many brightening serums.
“Vitamin C is an amazing antioxidant that is beneficial for patients with hyperpigmentation,” explains Dr. Green. “It works by brightening hyperpigmented spots on the skin, but not lightening normal skin.”
Dr. Green says to avoid vitamin C if you have allergies or sensitive skin since it can cause redness, irritation and tingling.
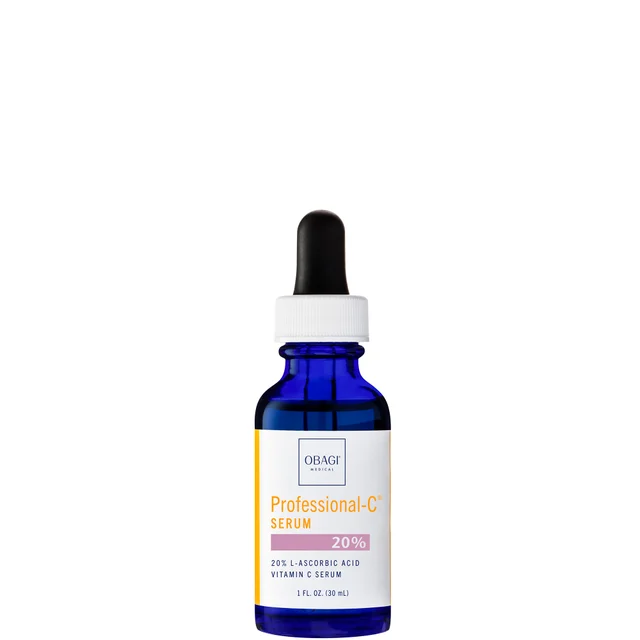
Try:Obagi Medical Professional-C Serum 20%
4. Arbutin
According to Dr. Green, “Arbutin is a natural form of hydroquinone derived from the bearberry plant. It is a safer and effective alternative to hydroquinone and is less cytotoxic to the melanocytes.” Use it gradually during the first few weeks to make sure your skin doesn’t react. You can then increase the frequency of use. Also, as always, make sure you are wearing sunscreen.
Even though it’s considered natural, avoid arbutin if you are pregnant because it is a derivative of hydroquinone, notes Dr. Evans.
Try:Sunday Riley TIDAL Brightening Enzyme Water Cream
5. Willow Bark Extract
“Willow bark extract is a beta hydroxy acid that helps to exfoliate the skin and encourage cell turnover,” Dr. Evans says. That’s because it’s related to salicylic acid, Dr. Green adds. “White willow-bark extract is composed of salicin, the natural form of salicylic acid,” she says. “Salicylic acid helps to shed dead skin cells from your skin to allow new and healthy skin cells to regenerate.”
You can find willow-bark extract in spot treatments, serums and exfoliating peels. Products like spot treatments can be used daily, while exfoliating peels should only be used once or twice a week.
Try:iS Clinical Brightening Complex
6. Licorice
“Licorice root contains two ingredients that help with pigmentation: glabridin and liquiritin,” explains Dr. Green. “Glabridin helps to retrain tyrosinase, an enzyme that produces melanin, which leads to pigmentation. Liquiritin helps to break up and remove melanin and pigmentation in the skin.”
In addition to tackling dark spots, licorice can be soothing and help even out your skin tone. Look for it in products like serums, and use daily for best results.
Try:Eminence Organic Skin Care Bright Skin Licorice Root Booster-Serum
7. Mulberry Extract
Mulberry extract is a natural but powerful brightening agent derived from the mulberry plant, notes Dr. Erum Ilyas, a board-certified dermatologist and founder of Amber Noon in Pennsylvania. “Mulberry plants have several compounds that have been extracted from both roots and stems, with known ability to block tyrosinase, the enzyme involved in the production of melanin,” she adds.
Some studies have shown mulberry extract to be as powerful as kojic acid (see above)—another common natural brightener. If your skin doesn’t agree with kojic acid or is sensitive, Dr. Ilyas says that mulberry extract is generally well tolerated and won’t likely cause irritation.
Try:PCA SKIN Vitamin B3 Brightening Serum
8. Lactic Acid
If you have sensitive skin or are just looking for something mild, products containing lactic acid may be what you need. “Lactic acid is derived from sour milk and is an alpha hydroxy acid, so it is one of the mildest ingredients you can use for skin lightening,” Dr. Green says. “Gentle enough for sensitive skin, lactic acid penetrates the skin, causing mild exfoliation. It’s also a melanin suppressor.”
She notes that because it decreases your melanin production, you should wear sunscreen and protective clothing to shield the treated areas from sun damage.
Try:Dr. Dennis Gross Clinical Grade IPL Dark Spot Correcting Serum
How to Use Dark Spot Lighteners the Right Way
Even naturally derived ingredients can be powerful, so it’s important to use brightening products with care. Here are a few tips to remember:
- Always patch-test any new product in a small, inconspicuous area and wait a day or two to see how your skin reacts before applying to a larger area of skin or your full face.
- When adding a product with alpha or beta hydroxy acids to your routine, start by using it once or twice weekly and allow your skin to adapt before working up to more frequent use.
Take care when using multiple products with active ingredients at the same time. Pick one targeted treatment to use as part of your morning or nightly regimen, and keep the rest of your routine simple to avoid overstressing your skin. Apply your skin care products in the correct order. Treatments like serums should be applied to clean skin to get the most benefit from their ingredients. Layer on moisturizer and sunscreen after. Speaking of sunscreen, make sure to wear SPF every day (yep, even on cloudy ones). Sun exposure contributes to worsening unwanted pigmentation, so going unprotected will undo the effects of your brightening regimen.
Risks & Benefits
As with all skin care products, there's a risk of allergic reaction to ingredients used in brightening products (which is why a patch test is so important). Some brighteners can also make skin more sensitive to the sun and irritation. For most people, using the products correctly will mitigate the risks and make it possible to reap the many benefits. Benefits include a reduction in the look of the following pigmentation issues:
- age spots
- post-inflammatory pigmentation (such as post-acne marks)
- scarring
- sun damage (some types of freckles)
- melasma

From the latest hair and makeup trends to the best solutions for your skin issues, we've got all your beauty concerns covered!